1.33 BMP C208 - Triangular Silt Dike (Geotextile-Encased Check Dam)
Triangular silt dikes (TSDs) may be used as check dams, for perimeter protection, for temporary soil stockpile protection, for drop inlet protection, or as a temporary interceptor dike (refer to Figure 3 - 16: Sediment Barrier – Geosynthetic Dike).
TSDs may be used on soil or pavement with adhesive or staples.
TSDs have been used to build temporary:
◦ concrete wash out facilities
1.33.3 Design and Installation Specifications
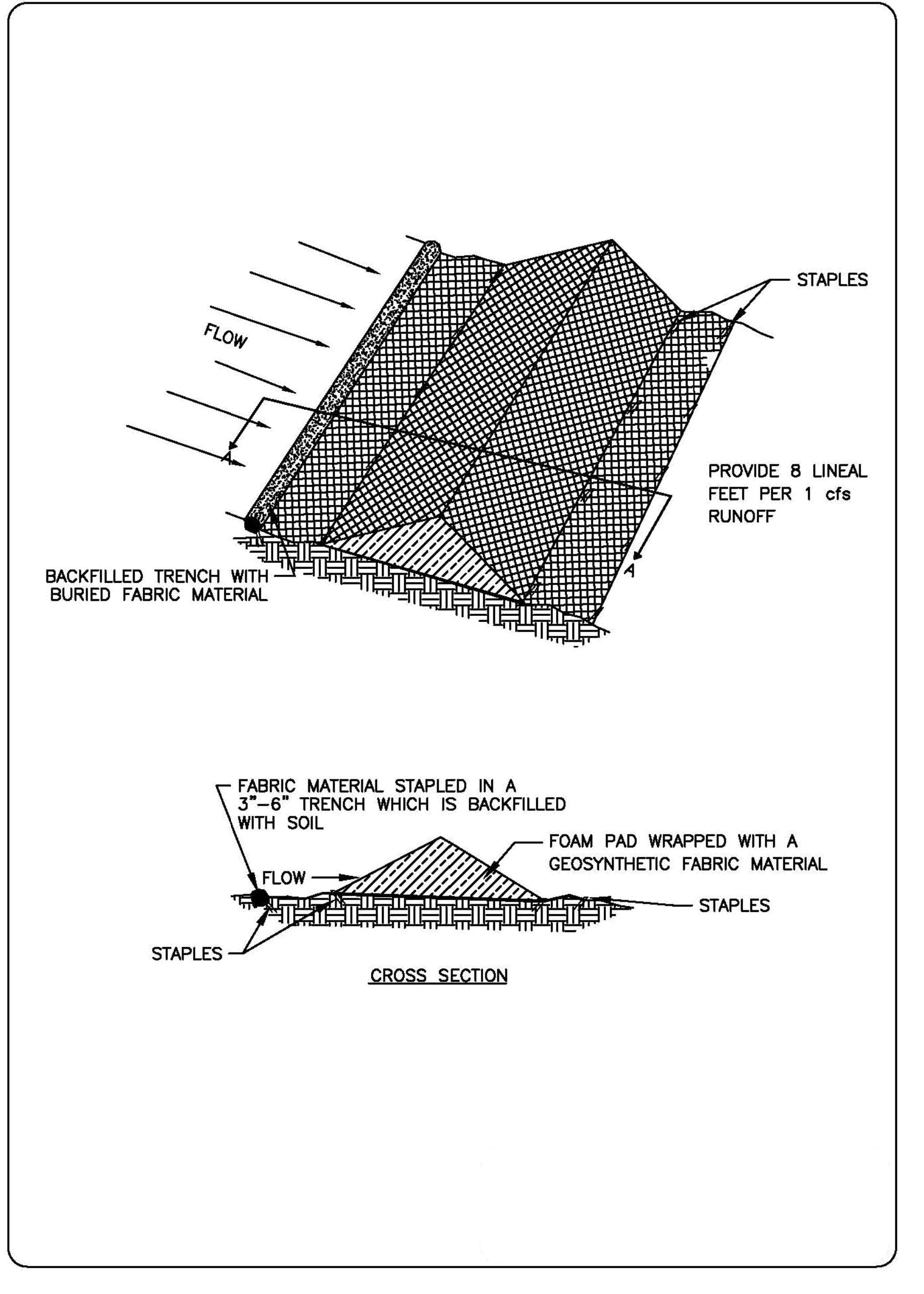
TSDs are made ade of urethane foam sewn into a woven geosynthetic fabric.
It is triangular, 10 inches to 14 inches high in the center, with a 20-inch to 28-inch base. A 2–foot apron extends beyond both sides of the triangle along its standard section of 7 feet. A sleeve at one end allows attachment of additional sections as needed.
Install with ends curved up to prevent water from flowing around the ends.
The fabric flaps and check dam units are attached to the ground with wire staples. Wire staples should be No. 11 gauge wire and should be 200 mm to 300 mm in length.
When multiple units are installed, the sleeve of fabric at the end of the unit shall overlap the abutting unit and be stapled.
TSDs should be located and installed as soon as construction will allow.
TSDs should be placed perpendicular to the flow of water.
The leading edge of the TSD must be secured with rocks, sandbags, or a small key slot and staples.
Monitor triangular silt dikes for performance and sediment accumulation during and after each runoff producing rainfall. Remove sediment when it reaches one half the height of the dam.
Anticipate submergence and deposition above the triangular silt dam and erosion from high flows around the edges of the dam. Immediately repair any damage or undercutting of the dam.
In the case of grass-lined ditches and swales, remove check dams and accumulated sediment when the grass has matured sufficiently to protect the ditch or swale, unless the slope of the swale is greater than 4 percent. Seed and mulch the area beneath the check dams immediately after dam removal.
Figure 3 - 16: Sediment Barrier – Geosynthetic Dike